exit()
-싱글스레드 환경에서 프로그램 종료 시 사용된다.
-exit()를 호출하더라도 프로그램이 바로 종료되지 않고 다음의 경우 객체의 소멸자가 호출된다.
--전역 정적 클래스 객체를 생성한 경우
--전역/지역 싱글톤 동적 객체를 사용한 경우 (클래스 정적 변수에 할당)
quick_exit()
-exit()를 멀티스레드 환경에서 사용하면 글로벌/정적 객체들은 스레드 종료 없이 소멸되려고 한다.
-멀티스레드 환경에서 정상적으로 에러코드를 반환하고 프로그램을 종료하기 위해 quick_exit()를 호출해야 한다.
-quick_exit() 호출 시 각 객체의 소멸자를 호출하지 않는다.
--위의 exit()에서 소멸자가 호출되는 경우에도 quick_exit()는 소멸자 호출없이 바로 종료된다.
abort(), std::terminate()
-처리되지 않은 예외가 발생할 경우 자동으로 호출된다.
-기본적으로, terminate()는 abort()를 호출한다.
-커스텀 핸들을 지정하기 위해 set_terminate() 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
예제 소스코드를 통해 실제로 결과를 관찰해본다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
class Person {
public:
Person()
:age(0)
, name("Kim")
, isContinue(false)
{
cout << "Person constructor" << endl;
start();
};
~Person() {
cout << "Person destructor" << endl;
stop();
};
void start() {
cout << "Person start" << endl;
mainMutex.lock();
if (isContinue) return;
thread = std::thread(std::bind(&Person::run, this));
while (!isContinue) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(10ms);
}
mainMutex.unlock();
}
void stop() {
cout << "Person stop" << endl;
if (isContinue) {
//isContinue = false;
if (thread.joinable()) {
thread.join();
}
}
}
void run() {
cout << "Person run" << endl;
isContinue = true;
int cnt = 0;
while (isContinue) {
cout << "running..." << endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
}
}
static std::shared_ptr<Person> get_instance();
private:
string name;
int age;
bool isContinue;
std::thread thread;
std::mutex mainMutex;
static std::shared_ptr<Person> instance;
};
std::shared_ptr<Person> Person::instance;
std::shared_ptr<Person> Person::get_instance() {
cout << "get_instance call" << endl;
if (instance.get() == NULL)
instance.reset(new Person());
return instance;
}
std::shared_ptr<Person> temp(Person::get_instance());
void main() {
cout << "Program start" << endl;
exit(0);
//std::quick_exit(0);
}
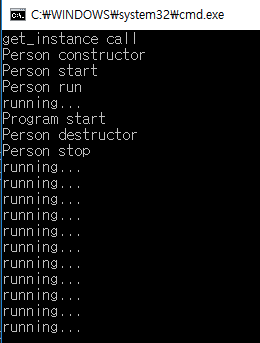
exit(0)을 호출했음에도 불구하고 Person 클래스 소멸자에서 isContinue를 false로 지정하지 않아 스레드 run()이 계속 작동하는 모습이다.
다음은 quick_exit(0)을 했을 때의 결과이다.
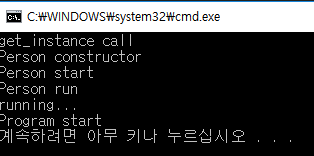
quick_exit(0) 호출 즉시 프로그램이 종료되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
결론: 멀티스레드 환경에서 프로그램을 즉시 종료하고자 한다면, quick_exit(0) 또는 quick_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS)를 호출하자.
'컴퓨터 공학 > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ 함수 내 람다 함수를 통해 코드 정리 (0) | 2019.11.14 |
|---|---|
| const_cast 사용 예시 (0) | 2019.11.14 |
| c++ unordered_map 사용 예시 (0) | 2019.04.06 |
| [C/C++] 윈도우즈 운영체제에서 맥 주소 가져오기 (0) | 2018.09.18 |
| [c/c++] Boost 주요 기능 정리 (0) | 2018.09.12 |